By Hannah Schwartz
Reducing waste is a cornerstone of sustainable practice for universities worldwide. By minimizing their ecological footprint, institutions not only contribute to a cleaner, healthier environment but also demonstrate a commitment to responsible stewardship. From conserving natural resources to saving costs and inspiring future generations, waste reduction in universities serves as a powerful beacon for sustainable living and a greener future.
With this in mind, STARS* asks universities to assess their waste production.
STARS aligns the criteria of waste reduction with the following United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDG).
- Goal 3 – Ensuring healthy lives & promoting well-being for all at all ages. In addition, this goal strives to increase access to healthcare worldwide.
- Goal 6 – Ensure the availability & sustainable management of water & sanitation for all. This goal strives to ensure equitable access, improve quality, & increase efficiency of water & sanitation systems.
- Goal 11 – Making cities & human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, & sustainable. This goal strives to improve living standards & resilience, ensure economic resources & rights, & implement sound policies.
- Goal 12 – Ensuring sustainable consumption & production patterns. This goal strives to decrease waste, use & reuse resources efficiently, & adopt zero-waste practices.
- Goal 14 – Conserving & sustainably using the oceans, seas, & marine resources for sustainable development. This goal strives to prevent marine pollution, protect & conserve ecosystems, & end destructive fishing.
Subcategories:
- Waste Minimization and Diversion – This credit recognizes institutions that are minimizing waste production, diverting materials from landfills and incinerators, and conserving resources by recycling and composting. This credit applies to all institutions. It attempts to measure the reduction in total waste per person from the base year to the performance year, the total waste produced per person, and waste diverted from the landfill or incinerator. Each part is scored independently and calculated using formulas based on total waste generated from the base year and the performance year, as well as total waste generated (diverted & disposed) and weighted campus users of the performance year.
- Auburn’s score: 4.74/8
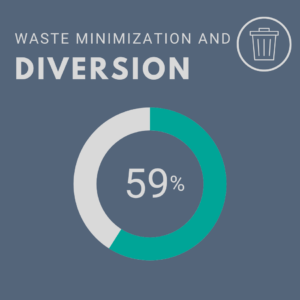
- Auburn’s score: 4.74/8
- Construction and Demolition Waste Diversion – This credit recognizes institutions that have diverted construction and demolition (C&D) wastes. C&D is a significant source of waste that falls outside of an institution’s standard waste stream and may be handled by a separate contractor or waste hauler. This credit applies to all institutions that have conducted a major construction, renovation and/or demolition project in the three years prior to submission. An institution earns the maximum of 1 point available for this credit by diverting all its non-hazardous construction and demolition waste from the landfill or incinerator in a one-year period. Incremental points are awarded based on the percentage of waste that is recovered.
- Auburn’s score: 0.88/1
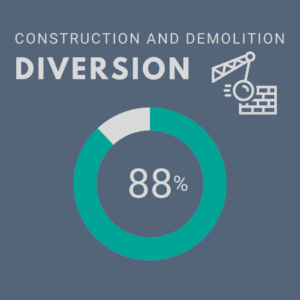
- Auburn’s score: 0.88/1
- Hazardous Waste Management – This credit recognizes institutions that seek to minimize and safely dispose of all hazardous, universal, and non-regulated chemical waste and that have electronic waste (e-waste) recycling and/or reuse programs. Given the environmental and workplace health hazards that arise from hazardous waste disposal and e-waste recycling, this credit is reserved for programs that take steps to ensure that workers’ basic safety is protected, and environmental standards are met. Each credit is scored separately based on meeting certain criteria related to hazardous waste minimization and disposal and electronic waste diversion.
- Auburn’s score: 0.75/1

- Auburn’s score: 0.75/1
Reflection:
The university participates in the GameDay Recycling Challenge and Campus Race to Zero Waste – nationwide competitions to help colleges and universities advance campus recycling and waste reduction efforts. The campus community receives information about the university’s recycling program via outreach events, signage, campus newsletters, web, social media, etc. Recycling bins are labeled with acceptable, and in some cases, unacceptable, materials (words and pictures). Auburn recycles the following materials:
- Paper, plastics, glass, metals
- Food
- Electronics
- Residence halls move-in/move-out waste
- Scrap metal
- Pallets
- Tires
- Batteries
Auburn has established processes and procedures to minimize the volume and toxicity of hazardous, special, universal, and non-regulated chemical wastes generated through University operations. Auburn continuously seeks new opportunities to improve performance in this area. Auburn University Risk Management & Safety (RMS) manages all hazardous, universal, and non-regulated chemical waste generated by university operations. As a part of this program, laboratory staff can designate chemicals in their inventory as available for redistribution.
Auburn University can improve waste management by enhancing recycling programs campus-wide, promoting reusable dining ware, and organizing regular clean-up events. We could also implement training and awareness programs for hazardous waste used in labs. These could be kept on a website that details how to handle these materials. These steps will reduce landfill waste, foster sustainability, and inspire a culture of responsible waste management among students and staff.
*The Sustainability Tracking, Assessment, and Rating System (STARS) program is a self-reporting framework for institutions of higher education to track their sustainability performance created by the Association for the Advancement of Sustainability in Higher Education. Overall, STARS is made up of 211 possible points in 64 different subcategories. The subcategories are grouped by Academics, Engagement, Operations, and Planning & Administration. Additionally, participants may receive extra points for exemplary and innovative practices. In this summary, our score is shown over the amount of possible points for each credit. View Auburn University’s 2022 STARS Report for more details.
Learn about the SDGs & AU and our contributions related to this post









