Human behavior is influenced by the environment in which it resides. The average worker spends the most amount of time every day at work. That accumulates to 90,000 hours in the workplace over the course of their life. Therefore, the workplace environment is a significant factor in the lifetime well-being of workers.

Gallup estimates that 15% to 20% of total payroll cost is due to turnover often caused by burnout, a $322 billion loss globally in productivity due to turnover and burnout, and 75% of medical expenses come from preventable conditions. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines a healthy workplace as “one in which workers and managers collaborate to use a continual improvement process to protect and promote the health, safety, and well-being of all workers and the sustainability of the workplace.”
Thankfully there are regulatory minimum safeguards on workplace safety. Still, it is up to the institution how they implement other aspects of workplace well-being, namely promotion and improvement of safety standards. STARS¹ attempts to tackle this issue by assessing the institution’s compensations, protections, benefits, and other assistance offered to workers. An apt description of the importance of workplace safety comes from STARS’ technical manual. “An institution’s people define its character and capacity to perform; and so, an institution’s achievements can only be as strong as its community.”
This assessment aligns with the United Nations Sustainability Development Goals:
Goal 1: End poverty in all its forms everywhere.
Goal 3: Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages
Goal 8: Promote sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment, and decent work for all
Subcategories
- Employees Compensation: This credit acknowledges institutions where all employees’ and contractors’ compensation meets the living wage standard. This ensures that even the lowest-paid employee can meet their basic needs.
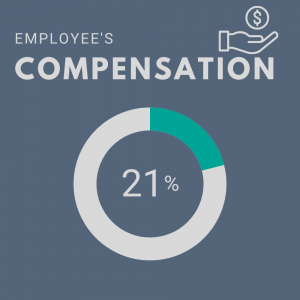
Auburn’s Score: 0.63/3
- Assessing Employee Satisfaction: To earn this credit, institutions must have an evaluation program for employee satisfaction and engagement. This assessment can help an institution identify its strengths as well as opportunities for improvement.

Auburn’s Score: 1/1
- Wellness Programs: This credit rewards institutions that provide wellness programs, such as counseling, for students and employees and provides a smoke-free campus.

Auburn’s score: 1/1
- Workplace Health and Safety: This credit recognizes institutions with robust systems to minimize injuries and occupational hazards.
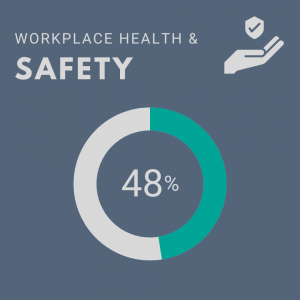
Auburn score: 0.95/2
Reflections
Our perfect scores for assessing employee satisfaction and wellness programs are well-earned. The assessment, which was done with the help of COACHE for faculty and through Mercer for non-faculty, was thorough, representative, and actionable. Regarding wellness programs, Auburn offers various programs ranging from counseling to health classes, and medical clinics for students and employees. As for compensation, at the time of this latest STARS assessment, 96% of employees were receiving a living wage, Auburn had just committed to increase the pay to what would’ve been a living wage starting in 2022.
Our main areas for improvement are compensation and workplace health and safety. We scored higher than many of our peer institutions in employee compensation, but that could change this year. The cost of living has significantly increased since the initial push for a new minimum of $18.84 and $14.50 for part-time employees. In the fiscal year 2023, Auburn Human Resources announced that, with the help of the Mercer study, they would be adjusting compensation to more accurately reflect market rates while ensuring no one‘s compensation is reduced. However, this lacks a standard living wage minimum for every employee. According to the MIT Living Wage Calculator, the May 24, 2023, living wage is set at $23.09 for a family of four with both parents working in the Auburn-Opelika metro area, which is the measurement standard that STARS requires to receive full points. It is yet to be seen if every employee will receive such an adjustment. Additionally, to receive full credit, the lowest-paid employee’s compensation must meet 150% of the local living wage, and 100% of contractor employees must be paid a living wage or be under a collective bargaining agreement. Achieving full points for the compensation credit certainly seems difficult here on campus, but a living wage minimum appears much more approachable.
The true avenue for improvement on this credit can come from better occupational health and safety practices. STARS wants to see the use of a nationally or internationally recognized occupational safety and health management system such as OSHA. We currently use various management systems and best practices derived from OSHA and others, but our state doesn’t require usage of those national and international standards by state organizations. Texas A&M is a peer school that uses OSHA guidelines as well as International Organization for Standardization and American National Standards Institute. They received a 63% higher score and had half the incidents per 100 employees. This is significant because STARS bases the score on 1. If you have an internationally or nationally recognized system, and 2. the percentage of recordable incidents per 100 full-time employees. The safety and health of employees are especially important, and there is a direct way to improve upon that score. With the adoption of these standards, there should be a tangible improvement to our score but, more importantly, the safety of all Auburn employees.
¹The Sustainability Tracking, Assessment, and Rating System (STARS) program is a self-reporting framework for institutions of higher education to track their sustainability performance created by the Association for the Advancement of Sustainability in Higher Education. Overall, STARS is made up of 211 possible points in 64 different subcategories. The subcategories are grouped by Academics, Engagement, Operations, and Planning & Administration. Additionally, participants may receive extra points for exemplary and innovative practices. In this summary, our score is shown over the amount of possible points for each credit. View Auburn University’s 2022 STARS Report for more details.
Learn about the SDGs & AU and our contributions related to this post.





