by Randy Martin, Office of Sustainability
Thousands of students attend universities and colleges for primarily one purpose, academics. Academics serve as the backbone of an institution. There are many things that people do and participate in tangentially to classes, but at the root, the university experience is in the classroom. That is why ¹STARS rates institutions on their implementation of sustainability principles within the classroom. According to STARS, universities need to train, connect, and teach students sustainability in their classroom context.
Sustainability isn’t a concept or practice that can be left to a few professionals. Every profession and sector needs to practice sustainability. Each sector has its own sustainability challenges and needs, where better to teach and discuss those issues than in the classroom? That way, new generations will have the skills, mindset, and ethics to implement sustainability in their industry and to solve their industries’ major problems.
According to STARS, implementing sustainability teaching in the classroom coincides with UN Sustainable Development Goals:
- 4: Ensure inclusive and quality education for all and promote lifelong learning
- 13: Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts
Subcategories
This category consists of eight subcategories worth a total of 40 points
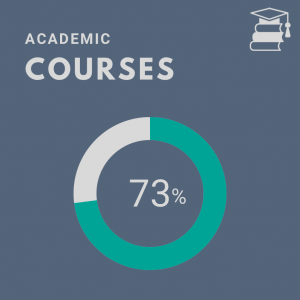
 Academic Courses: At the most basic level, institutions need to be teaching sustainability in the classroom. This is where students are prepared and ready to learn. This is a powerful avenue to teach concepts and ideas. To get full points on this subcategory, institutions have to have sustainability courses and content in multiple (ideally all) departments to comprehensively cover sustainability topics in varied fields.
Academic Courses: At the most basic level, institutions need to be teaching sustainability in the classroom. This is where students are prepared and ready to learn. This is a powerful avenue to teach concepts and ideas. To get full points on this subcategory, institutions have to have sustainability courses and content in multiple (ideally all) departments to comprehensively cover sustainability topics in varied fields.
 Auburn’s Score: 10.26/14
Auburn’s Score: 10.26/14- Learning Outcomes: A student earns a degree by displaying knowledge of the university’s set learning outcomes. STARS awards this credit as a proportion of students that are required to have an understanding of sustainability to graduate.
Auburn’s Score: 0.88/8  Undergraduate Programs: Dedicated sustainability programs can provide students with the depth and breadth needed to face and solve sustainability challenges. Institutions receive points for this credit when they have undergraduate programs focused on sustainability.
Undergraduate Programs: Dedicated sustainability programs can provide students with the depth and breadth needed to face and solve sustainability challenges. Institutions receive points for this credit when they have undergraduate programs focused on sustainability.
Auburn’s Score: 3/3- Graduate Program: Graduate programs can go deeper than undergraduate programs. Dedicated
 programs allow students to become experts in different sustainability fields. Institutions that have graduate programs dedicated to sustainability are awarded this credit.
programs allow students to become experts in different sustainability fields. Institutions that have graduate programs dedicated to sustainability are awarded this credit.
Auburn’s Score: 3/3 - Immersive Experience: In-depth experiences, community-based internships, and study abroad programs can deepen and expand a student’s understanding of sustainability.
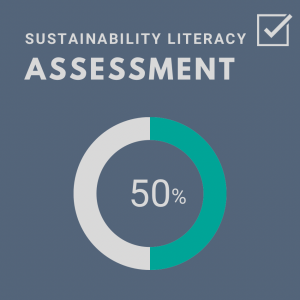 Auburn’s Score: 2/2
Auburn’s Score: 2/2 - Sustainability Literacy Assessment: Assessments can help institutions gauge and improve students understanding of sustainability.
Auburn’s Score: 2/4 - Incentives for Developing Courses: Academic staff need the support of the institution to expand
 sustainability in their courses. Institutions can provide development, training, funding, and other incentives.
sustainability in their courses. Institutions can provide development, training, funding, and other incentives.
Auburn’s Score: 2/2 - Campus as a Living Laboratory: Campuses are unique ecosystems of learning. Institutions have the ability to use their infrastructure as a medium for students to advance sustainability
 research and learning. Institutions that allow students to apply their sustainability learning to the campus infrastructure are awarded this credit.
research and learning. Institutions that allow students to apply their sustainability learning to the campus infrastructure are awarded this credit.
Auburn’s Score: 4/4
Auburn’s Total Score: 27.14/40
Reflections
Auburn overall does decently well in this category. We do a great job when it comes to academic offerings. For undergraduates, there is a dedicated sustainability minor as well as a few dedicated majors, such as Environmental Science and Biosystems Engineering. Graduate students have several options at the master’s and PhD levels. Additionally, students can participate in study abroad and community-based internship options.
Another area that we thrive in is our ability to utilize our campus for sustainability learning. Students have exceptional access to participate in solving sustainability problems on campus. Several projects, classes, capstones, and theses have changed the campus infrastructure and environment to make it more sustainable.
Finally, Auburn does well in offering incentives for faculty to improve sustainability learning in their courses. The (Re)Design workshop helps faculty conceptualize and implement new sustainability courses and sustainability learning outcomes for existing courses.
Where Auburn needs to improve is requiring students to meet sustainable learning outcomes. A few departments do this, but it only accounts for 11% of the student body. Auburn currently measures students for the following outcomes:
- Locate, evaluate, and use information
- Read and think critically
- Apply mathematical methods
- Write and revise for a variety of purposes
- Create and deliver oral presentations
- Analyze their own society and its relationship to the larger global context
- Interact in intercultural situations
- Apply scientific principles
- Analyze and value creative artistic endeavors
Auburn could and should add a specific sustainability learning outcome that would apply to the entire student body. Something similar to “Students will identify, act on, and evaluate their professional and personal actions with the knowledge and appreciation of interconnections among economic, environmental, and social perspectives,” which was pulled from the STARS technical document.
Auburn provides ample access to sustainability learning; it just isn’t required learning for the majority of students to graduate. If we want to markedly improve our score, we need to start by setting sustainability as a major learning outcome of the University.
Actions
Students:
- Look into courses, groups, or projects where you can have a tangible impact on the sustainability of Auburn’s campus.
Faculty
- Be on the lookout for the (Re)Design workshop slated for May 2023.

¹The Sustainability Tracking, Assessment, and Rating System (STARS) program is a self-reporting framework for institutions of higher education to track their sustainability performance created by the Association for the Advancement of Sustainability in Higher Education. Overall, STARS is made up of 211 possible points in 64 different subcategories. The subcategories are grouped by Academics, Engagement, Operations, and Planning & Administration. Additionally, participants may receive extra points for exemplary and innovative practices. In this summary, our score is shown over the amount of possible points for each credit. View Auburn University’s 2022 STARS Report for more details.
Learn about the SDGs & AU and our contributions related to this post.






